Cambodia Project
Timeframe
June 2020 to June 2025
Country Context
Cambodia has a largely agrarian economy and agriculture is a significant contributor to GDP (around 35%) and employs a large majority of the population. Crop production accounts for around half of the sector’s GDP, and livestock around 15%. Cambodia’s updated Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) establishes a conditional target of 41.7% reduction of emissions by 2030.
Following successive years of strong export-led economic growth, Cambodia achieved lower middle-income status in 2015 and plans to be an upper middle-income country by 2030. In 2022, agriculture accounted for 66% of total national GHG emissions, and livestock accounted for about 25% of agriculture GHG emissions. Demand for livestock products is expected to increase rapidly as populations, incomes and urbanisation rates increase. Livestock sector development plans project growing animal populations and promote improved productivity.
Livestock GHG emissions are projected to increase by 50% in 2020-2035, with almost 60% of the increase due to a growing cattle population.
-
Policies and programmes:Cambodia has implemented an effective National Biogas Programme since 2006, installing more than 25,000 domestic biogas units to date, and a National Biodigester Development Policy was issued in 2021. Biogas and composting of manure were listed in Cambodia’s NDC (2020), but no projects or programmes are in place to promote composting. Other improvements in livestock management (e.g. improved feed, breeding) were listed as adaptation priorities. These and other productivity-enhancing measures are promoted by the government on a relatively small scale, with larger investments significantly dependent on donor funding (e.g. ADB Cross-border Livestock Health and Value Chains Improvement Project, 2025-2029). Livestock sector development strategies did not address climate change issues and plans to increase animal populations and productivity would likely increase GHG emissions.
Capacities: Prior to this project, the General Directorate for Animal Health and Production (GDAHP), which is responsible for livestock sub-sector management in Cambodia, had limited experience of integrating climate change issues in sub-sector strategy, plans, and activities. GDAHP staff had limited capacity to engage on GHG management and adaptation issues. Ministry of Environment (MOE) had previously relied on international consultants for inventory compilation, and previous NDCs were drafted with minimal input from GDAHP. The agriculture sector climate change action plan (2023) noted that evidence-based estimates of GHG mitigation potential in the livestock sector were not possible due to lack of data and related knowledge. Research institutions were also not engaged on this topic.
-
There were two sub-projects in Cambodia. The first, supporting GDAHP, had two specific objectives:
Strengthen institutional and technical capacities for GHG inventory compilation, management, and reporting.
Strengthen capacities in the livestock sector to take effective actions in response to climate change.
The second, supporting RUA, aimed to
Provide data that directly contributes to an improved national GHG inventory using the IPCC Tier 2 method for cattle and pig emissions.
Strengthen capacities for direct measurement of methane emissions from cattle.
-
GHG inventory improvement:
The livestock GHG inventory (Tier 1 for all species, Tier 2 for cattle and pigs) has been improved. The improved Tier 1 inventory was reported in Cambodia’s 2024 BTR submission, and the Tier 2 inventories have been approved to be incorporated in the next submission due by December 2026.
Compared to previous inventories compiled by international consultants, GDAHP’s new role in inventory compilation is strongly supported by MOE and the FAO country office, which is delegated by MOE to compile the AFOLU inventory. GDAHP now has a team of people with the knowledge, skills, Excel-based tools, and SOPs required to update the inventory on a regular basis. GDAHP now also recognises the important role of the Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) in data collection and research to support inventory improvement.
The improved inventories show that total livestock emissions are 15% higher than previously estimated. This is due to higher emissions from cattle, while manure management emissions from pigs are 67% lower than previously estimated. These improved inventories have been directly used to support better targeting of policies and measures (see below).
Strengthened capacities for climate response:
In 2025, for the first time, the GDAHP team was directly involved in technical analysis and policy discussions on Cambodia’s NDC 3.0 update (Sep 2025). The improved inventories were used as the basis for assessing technical options and national potential for GHG mitigation. Importantly, the team has now realised the significance of improved cattle feeding and marketing for balancing sector productivity targets and GHG management.
Cambodia’s NDC 3.0 update also incorporates results on adaptation from the project’s assessment of livestock climate vulnerabilities and adaptation capacities. This assessment highlighted vulnerabilities in the growing commercial sector, as well as previously unrecognized risks, and the roles that GDAHP and other stakeholders can play in addressing those risks.
The project also supported GDAHP to provide training in composting to 388 farmers in 5 provinces. This is the first time GDAHP has implemented the national goal of promoting composting in practice. The initiative has provided valuable lessons for further development of policies and measures in support of this goal.
GDAHP is in the process of revising its 10-year Strategic Plan, and the GDAHP team have formulated recommendations to incorporate lessons on GHG management and adaptation in the forthcoming plan.
The GDAHP team have been discussing further climate-smart investments with development partners (e.g. GGGI, FAO) and at least one international company.
Core staff at RUA have a better understanding of livestock GHG issues and the potential for further research to inform policy and practice on GHG management.
Strengthened capacity for GHG measurement
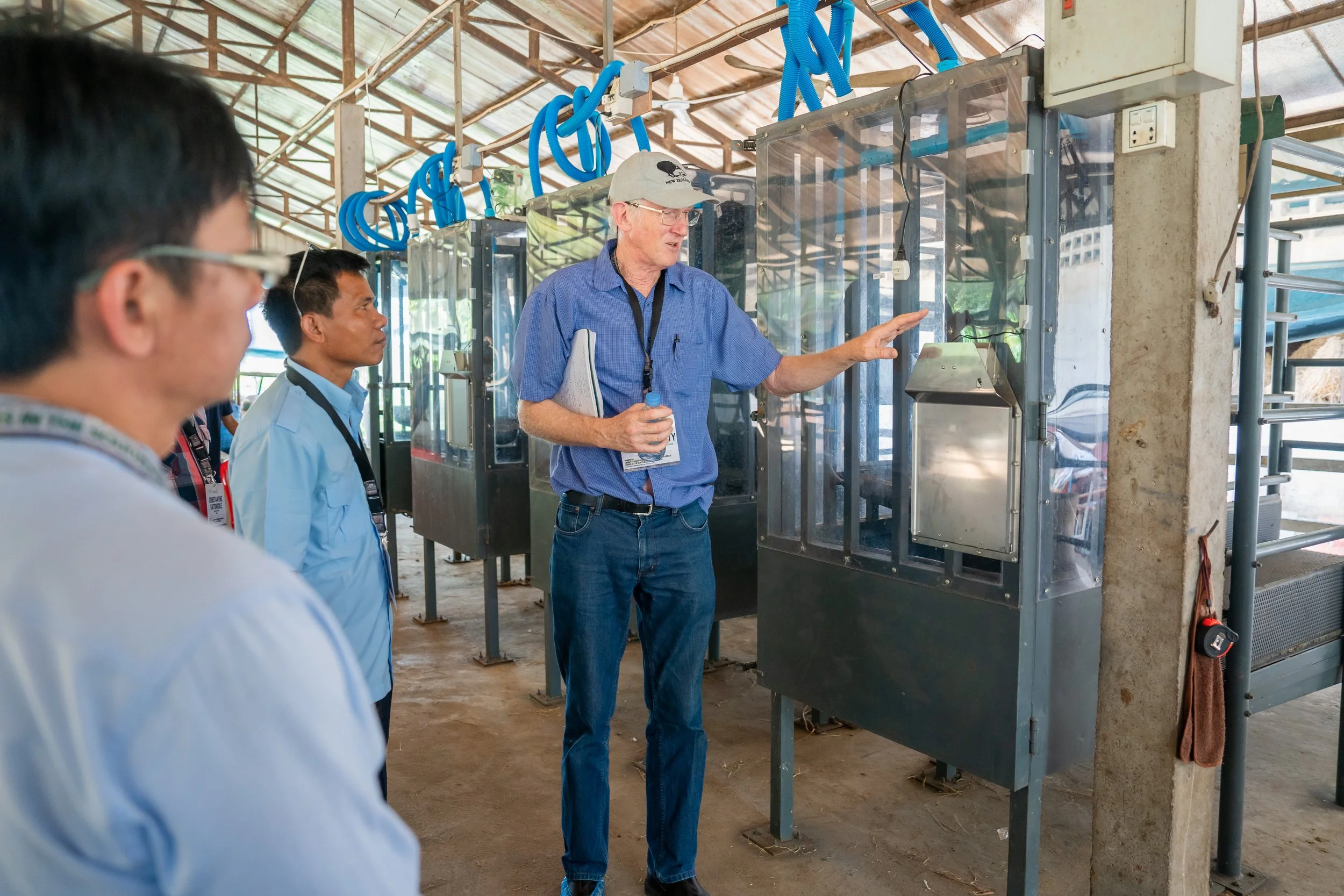
Before the NZCSA Initiative, there was no livestock GHG measurement capacity in Cambodia. Through the NZCSA, four headboxes & associated calibration and measurement equipment have been installed and developed with RUA. This has been matched with training of local RUA staff and students in use of the system. The international workshop held at RUA also enabled Cambodia to gain visibility as a regional location conducting GHG research and to contribute their knowledge and experience to the legacy documents for future users of this or similar systems.
-
Project activities have directly contributed to strengthening national capacities to set policy frameworks that support agricultural growth needs, enhance climate mitigation targets, and clarify government roles in adaptation to climate change. Compared to the starting point for the project, significant advances have been made in individual and institutional capacities to manage climate change in the livestock sector. GDAHP, which is mandated to manage climate change issues in the livestock sector, now has a good foundation to actively perform their role. The GDAHP team have directly contributed to mitigation and adaptation priorities in the updated NDC 3.0, and the GDAHP team are engaged in discussions on their next 10-year strategic plan. As national policies and plans continue to evolve, individuals, teams within key institutions and their leaders, and collaborative partnerships between key institutions are in place to enable evidence-based, stakeholder-inclusive deliberation on policy priorities and measures.
Strengthened GDAHP’s roles in promoting climate-smart investments and action: While the project directly engaged with small numbers of smallholders and actors in the private sector, the project’s focus was not on directly promoting uptake of climate smart practices. Through capacity building activities and engagement with farmers, GDAHP staff have gained more specific insights into challenges faced by farmers and the private sector, which helps them set priorities for their next steps in supporting climate action. For example, beyond promoting biogas on commercial pig farms as a general activity, GDAHP now recognises the importance to commercial farms of value-adding to bioslurry so that biogas is financially viable. As a ‘gatekeeper’ for donor support to the sector, and having significant convening power, GDAHP is now better placed to understand how practical needs relate to policy and investment planning, and their potential roles in supporting effective climate action on-farm.
Video introducing the Adaptation component of the project
Reports
Adaptation Options
Mitigation Options
Inventory improvement
Project Information
Dr. Kim Savoeun
Deputy Director General at General Directorate of Animal Health and Production, Cambodia (GDAHP)
“We are focused on the next step, on combining the information and using the new Tier 2 Inventory. We can use that data to understand what we need and to take action to reduce emissions of GHG.”
“Our government wants to take part in global climate action and we are proud that, with help of the New Zealand government, we can.”
Implementation Partners
General Directorate of Animal Health and Production (GDAHP), of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF)
Other In-country partners
MAFF Climate Change Technical Working Group
Ministry of Environment (Inventory office)
FAO Cambodia Country office

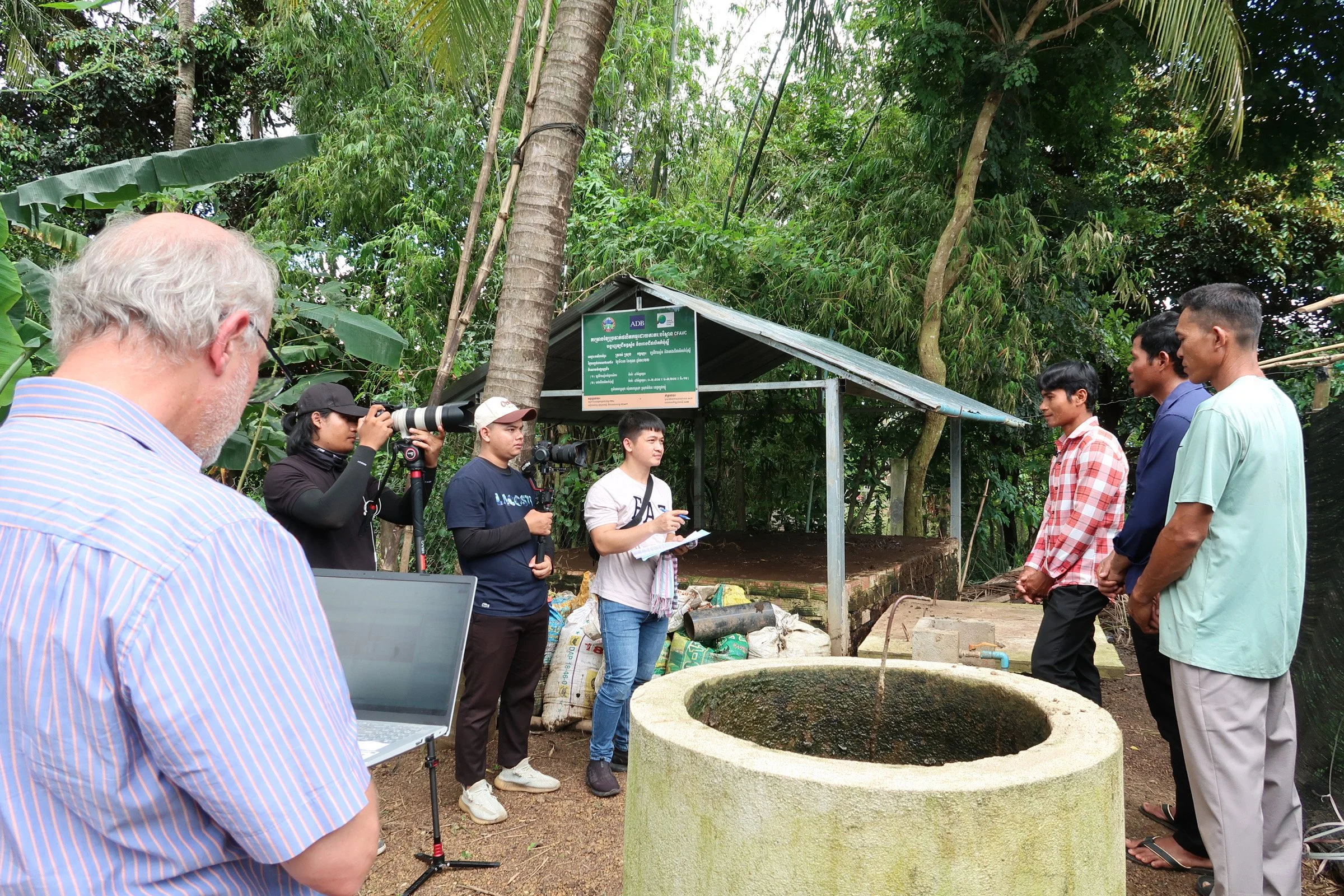
The four headbox chambers established by the NZCSA at the research station of Royal University of Agriculture, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, for methane yield measurements.
Mixing rice straw and para grass prior to feeding to cattle, part of the Mitigation study. This combination simulates the typical cattle diet in Cambodia. The study was able to reduce methane by adding coconut oil, which can suppress rumen protozoa and increase bacteria in the rumen while stimulating feed intake. (May 2025)

Students being trained to use the NZ supplied equipment at Cambodia's Royal University of Agriculture (21 Feb 2024).

NZ CSA achievements in adaptation, GHG inventory improvement and mitigation presented at NDC 3.0 planning meeting (FAO Cambodia office, MAFF Campus, Mar 2025).
A total of 15 training courses were conducted with a total of 388 farmers (of which 191 were women). Trainings were held across Kampong Speu, Kampong Cham, Tbong Kmum, Prah Vihear and Battambang provinces. The training participants were livestock farmers who also engaged in crop/vegetable cultivation.
Regional training event hosted by Cambodia’s RUA (Royal University of Agriculture) which made use of the NZ funded livestock measurement facility (Apr 2025).
Regional training event hosted by Cambodia’s RUA (Royal University of Agriculture) and made use of the NZ funded livestock measurement facility (Apr 2025).
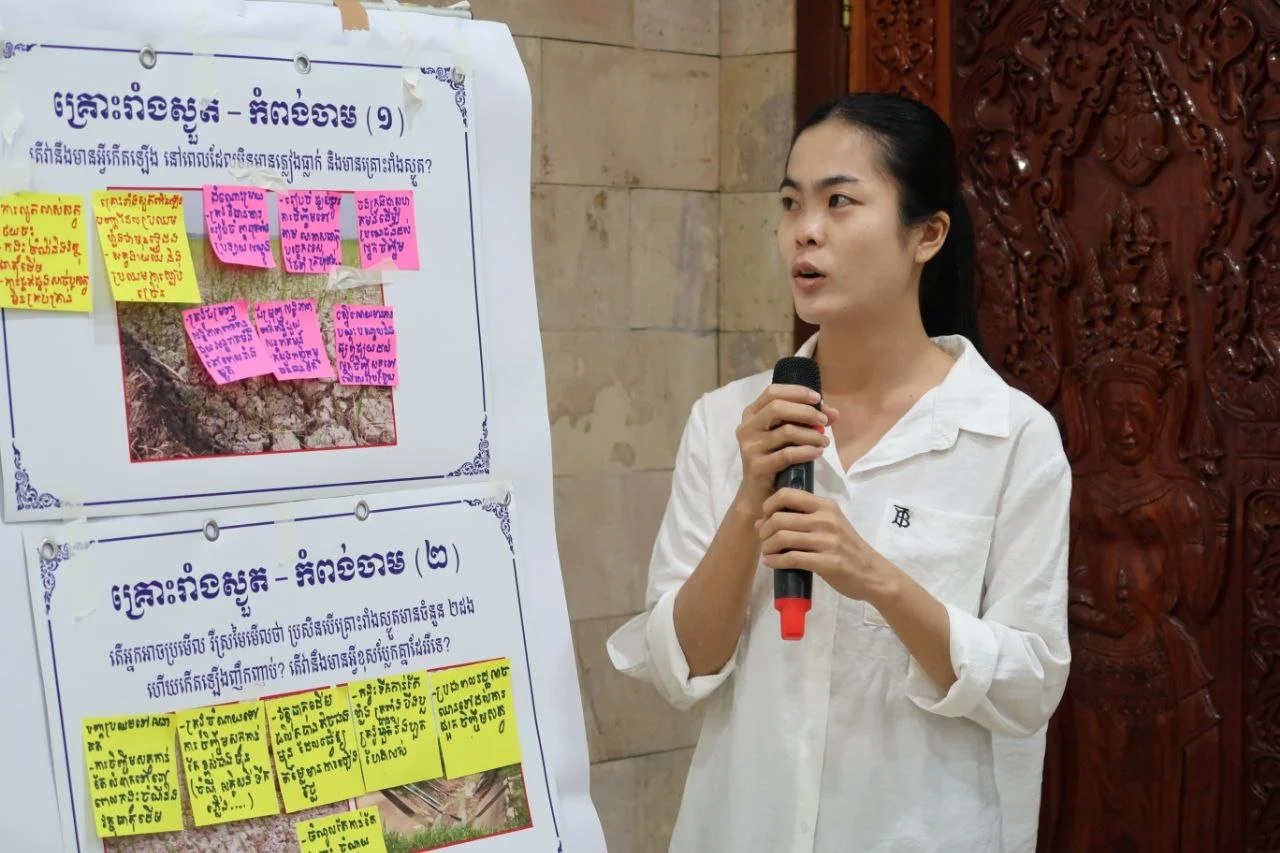
Livestock feed manufacturers contributing to the adaptation project. A powerful analysis of climate risks and “low hanging fruit” opportunities for addressing them efficiently.
Livestock researchers from all ASEAN partner countries met in Phnom Penh to consolidate the best available information on measurement of livestock greenhouse gases (Apr 2025).
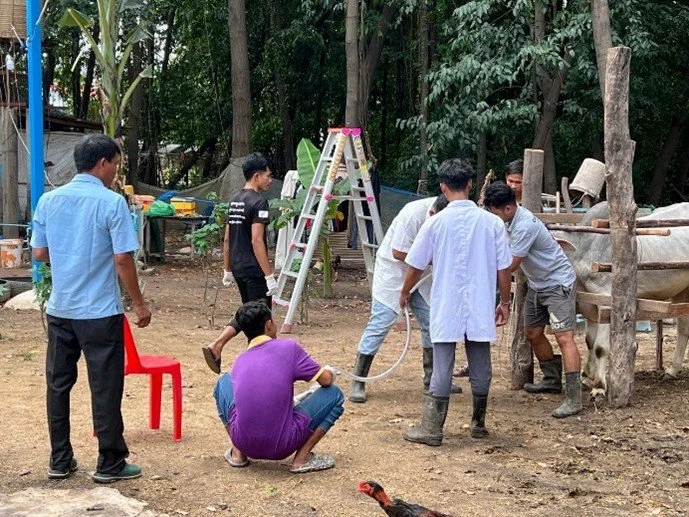
Training livestock farmers to understand the impacts of climate change and how to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through their daily activities, such as manure management through biogas and composting on their farms (Dec 2024).

English version of one of the farmer communication leaflets on animal waste management including the steps in biogas and compost production.

RUA team taking rumen sample from an experimental steer. Rumen fluid was collected 3 hours after feeding to compare the levels of protozoa and ammonia nitrogen and volatile fatty acid between different diets (Apr 2025)

Students being trained to use the NZ supplied equipment at Cambodia's Royal University of Agriculture (21 Feb 2024).

Students being trained to use the NZ supplied equipment at Cambodia's Royal University of Agriculture (21 Feb 2024).
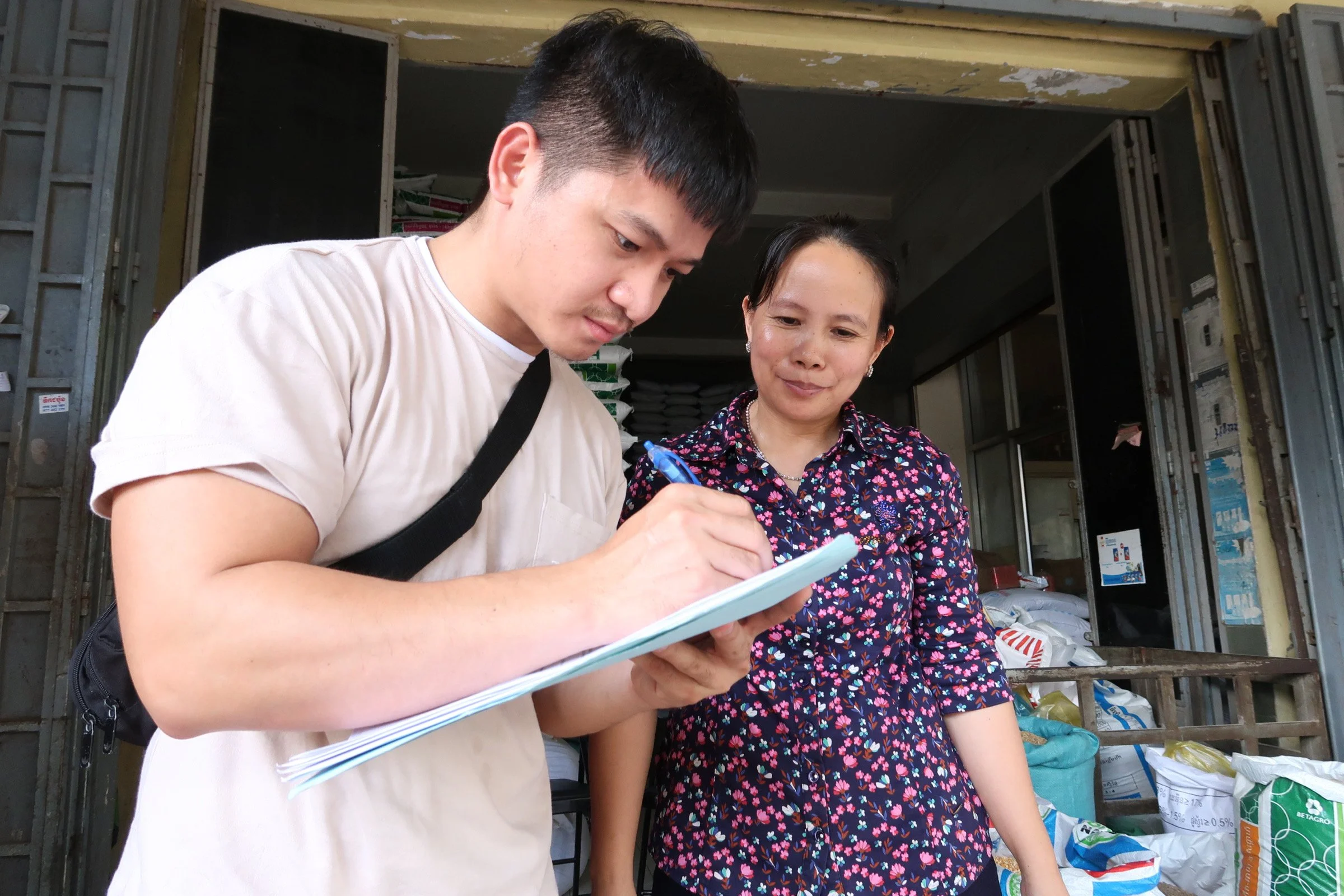
Livestock feed sellers contributing to the adaptation project. A powerful analysis of climate risks and “low hanging fruit” opportunities for addressing them efficiently.

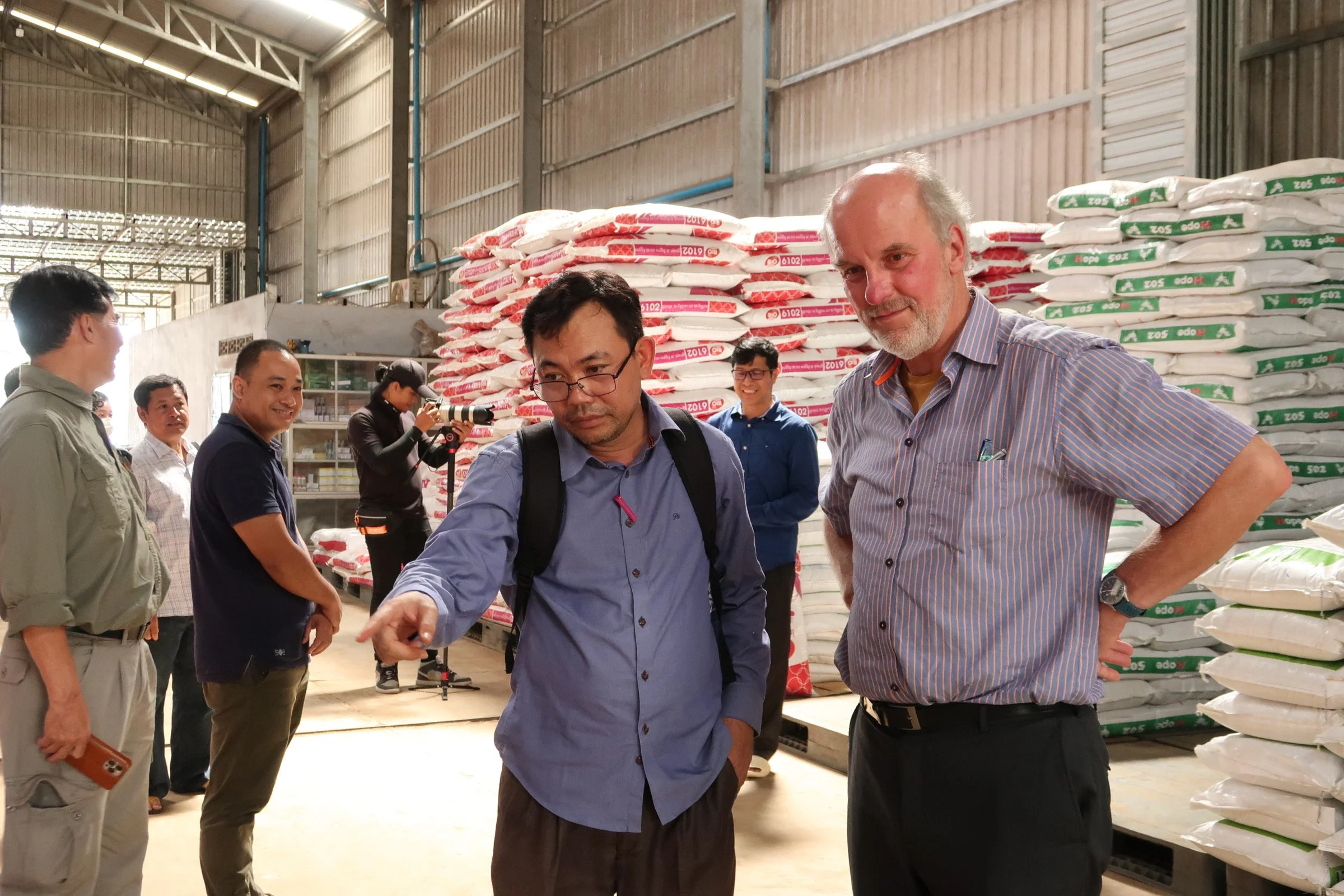
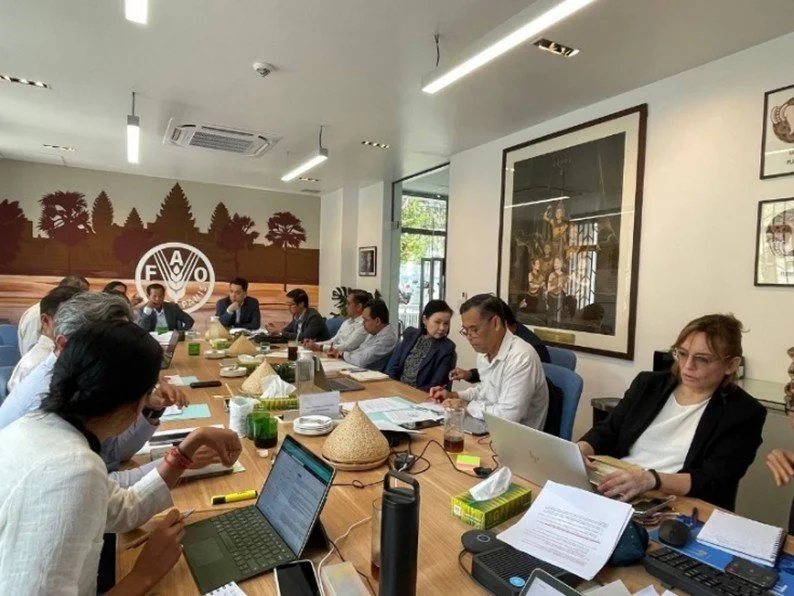
GDAHP together with NZAGRC consultant prepared for NDC 3.0 meeting (Mar 2025).

Cambodia researchers on a funded exchange trip to the headbox respiratory chambers at Can tho University, Vietnam (Jan 2024).
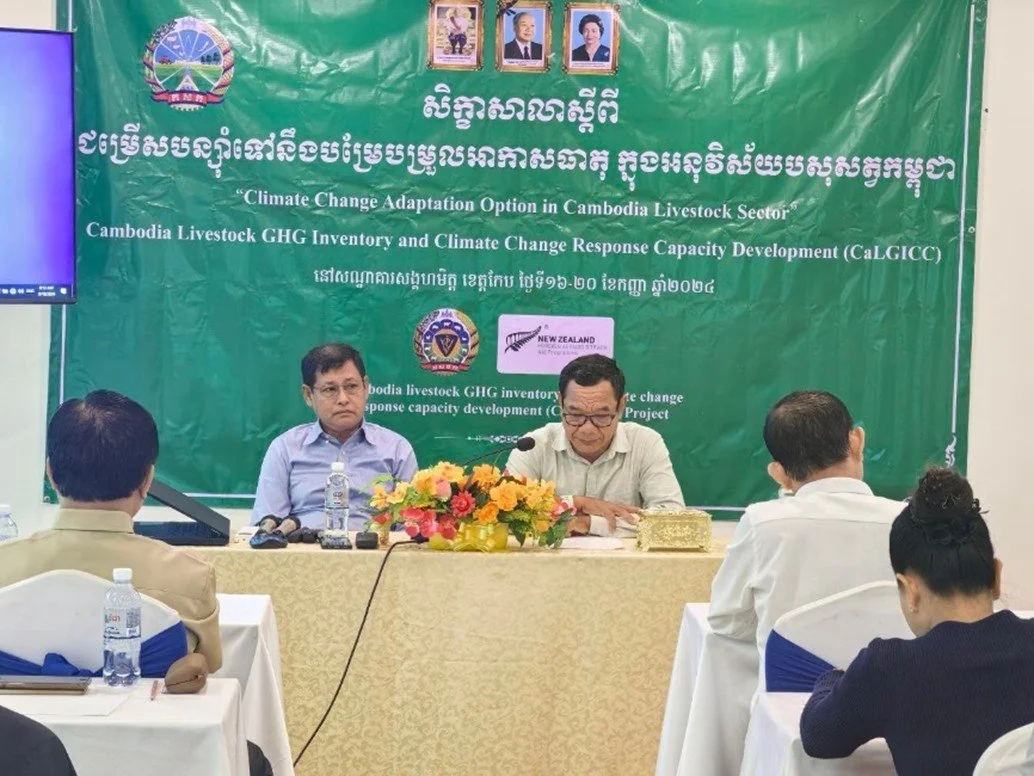

The 4 day training of trainers workshop to prepare officials for the training of farmers in animal production, health and waste management options to mitigate and adapt to climate change. Involved 16 participants from Department of Animal Production (DAP) and Department of Technical Extension and Legislation (DTEL) under GDAHP and Provincial Offices of Animal Health and Production (OAHPs) in Kep, Battambang, Prey Veng, Kampong Cham and Tbong Kmum provinces. (Sanghak Mit hotel in Kep province, 16-20 Sept 2024)
Behind the scenes of the summary video for the adaptation project.
Behind the scenes of the summary video for the adaptation project.